Understanding Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a common condition that causes pain and inflammation in the tendons on the outside of the elbow. Understanding the condition is essential for effective management and recovery. Tennis elbow can be a very painful condition and can keep one from doing even daily routines and simple tasks that we take for granted.
Definition of Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow is a type of tendinitis that occurs due to repetitive overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons. Despite its name, this condition can affect not only tennis players, but also individuals who engage in repetitive arm movements, such as painters, plumbers, and computer users.
Anatomy
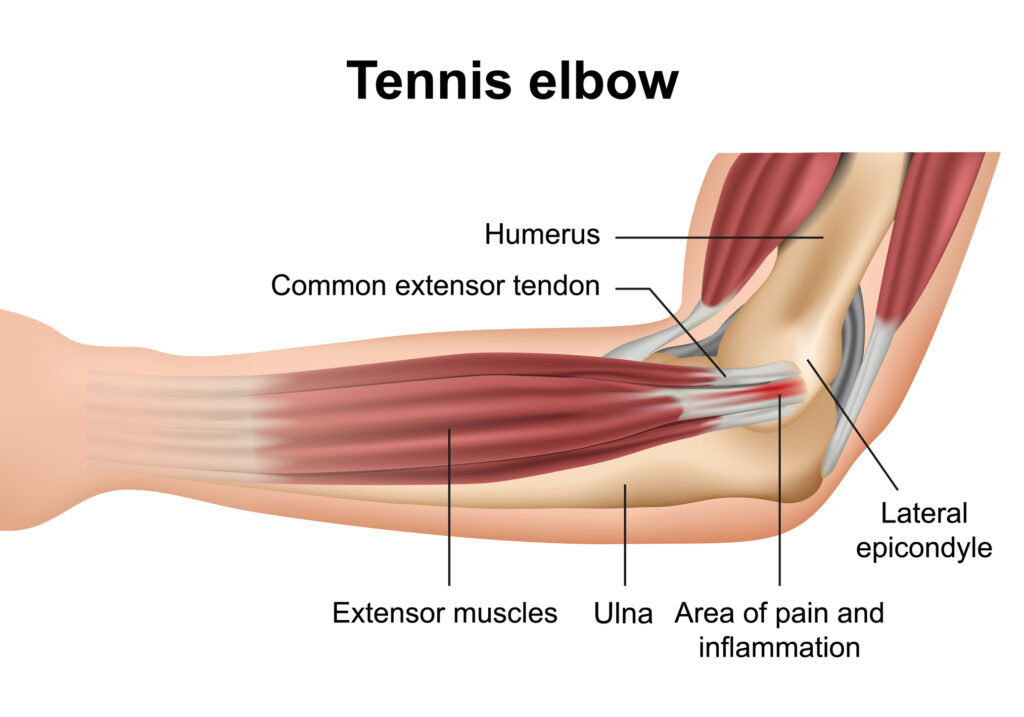
In the realm of your anatomy lies the elbow joint, a harmonious collaboration of three distinct bones: the humerus, which forms the upper arm, and the duo of bones in the forearm known as the radius and ulna. At the lowermost point of the humerus, one encounters protruding bony structures referred to as epicondyles, serving as the starting point for various muscles originating from the forearm. Notably, on the outer side of the elbow, one encounters the lateral epicondyle, a distinguished bony prominence. The cohesion of the elbow joint is maintained by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Tennis elbow injury medical vector illustration on white background eps 10
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, affects the muscles and tendons located in the forearm that facilitate the extension of the wrist and fingers. The extension of your wrist and fingers is carried out by the muscles in your forearm. These muscles are connected to the bone through tendons, commonly referred to as extensors. The extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) is the specific tendon frequently associated with tennis elbow.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of tennis elbow is the repetitive motion of the forearm muscles, which leads to microscopic tears in the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle (a bony prominence on the outside of the elbow). Some common risk factors include:
- Repetitive activities: Any repetitive arm motion, such as swinging a tennis racket or using a screwdriver, can strain the tendons and lead to tennis elbow.
- Improper technique: Poor form and incorrect equipment usage can contribute to the development of tennis elbow.
- Age and gender: This condition commonly affects individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, and it is slightly more prevalent in men than women.
- Occupational factors: People in occupations that involve repetitive arm movements are at a higher risk of developing tennis elbow.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of tennis elbow is pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow. It is most commonly diagnosed as an overuse injury or repetitive movement injury. The pain may radiate down the forearm and worsen with activities that involve gripping or lifting. Other signs and symptoms include:
- Weak grip strength
- Difficulty in fully extending the forearm
- Elbow stiffness in the morning
- Swelling or inflammation around the elbow
Diagnosing Tennis Elbow
To diagnose tennis elbow, a healthcare professional will perform a physical examination and discuss your symptoms and medical history. They may also recommend imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, to rule out other conditions. Additionally, they may perform specific tests to assess the strength and range of motion in your arm.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent or worsening elbow pain, it is advisable to seek medical attention. Early intervention and proper treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and promote a faster recovery. Your healthcare provider can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Common Symptoms of Tennis Elbow
The symptoms of tennis elbow can vary in intensity and may develop gradually over time. Here are the most common signs to look out for:
Pain and Tenderness
The primary symptom of tennis elbow is pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow. The pain may initially be mild and intermittent but can worsen with time, making it difficult to perform simple tasks that involve gripping or lifting objects.
Weakness and Stiffness
Individuals with tennis elbow may experience weakness in their affected arm, particularly when attempting to grip or carry objects. Stiffness in the elbow joint is also a common complaint, making it challenging to fully extend or flex the arm.
Radiating Pain
The pain associated with tennis elbow can radiate from the outer elbow down the forearm. It may extend towards the wrist and hand, causing discomfort during activities that involve wrist movements.
Worsening Symptoms
Without proper treatment and rest, the symptoms of tennis elbow can worsen over time. The pain may become constant, limiting the individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and negatively impacting their quality of life.
Treating Tennis Elbow
Effective treatment strategies can help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of the damaged tendons.
Rest and Modification of Activities
One of the first steps in treating tennis elbow is to rest the affected arm and avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Modifying your movements and avoiding repetitive motions can prevent further strain on the tendons and allow them to heal.
Pain Management Techniques
To manage pain associated with tennis elbow, various techniques can provide relief. These may include:
- Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day
- Taking over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Using topical pain-relieving creams or gels
- Employing techniques such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy or ultrasound therapy under the guidance of a healthcare professional
Physical Therapy Exercises
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process. A skilled physical therapist can guide you through exercises and techniques to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility in the forearm and wrist. These exercises may include:
- Eccentric exercises: These involve controlled lengthening of the forearm muscles to improve their capacity to absorb force.
- Wrist curls and extensions: Strengthening exercises targeting the wrist flexor and extensor muscles.
- Range of motion exercises: Gentle stretches to maintain or restore joint mobility.
- Grip strengthening exercises: Squeezing a stress ball or using a grip strengthening device to build forearm
Examination of injured elbow of tennis player
Use of Braces and Supports
Wearing a brace or forearm strap can provide additional support to the tendons and reduce strain on the affected area. These devices help alleviate pain and promote healing by limiting excessive movements and providing compression.
Corticosteroid Injections
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend steroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain. These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly into the affected area. However, they are typically used judiciously and in conjunction with other treatment modalities due to potential side effects.
Surgical Options (If Necessary)
Surgery for tennis elbow is considered only when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief over an extended period. The surgical procedure aims to remove damaged tissue and repair any underlying issues contributing to the condition.
An orthopedic surgeon will most likely have you obtain an x-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or Electromyography (EMG) before consulting you on surgery.
There are several surgical techniques used for treating tennis elbow, and the choice depends on the specific situation and the surgeon’s expertise. Here are a few common surgical options:
- Open Release Surgery: In this procedure, the surgeon makes an incision over the affected area and removes the damaged tendon tissue or any bone spurs that may be causing irritation. This technique allows for direct visualization and precise removal of the affected tissue.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized surgical instruments through small incisions. The surgeon can visualize the damaged tendon and remove it or repair it using small incisions, resulting in less tissue disruption and potentially faster recovery.
- Percutaneous Tenotomy: This technique involves the use of a needle-like instrument inserted through the skin to cut the damaged tendon. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and may be a suitable option for individuals who prefer a less invasive approach.
After surgery, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process. The specific rehabilitation program may vary depending on the surgical technique used and the individual’s condition. Physical therapy is commonly recommended to improve range of motion, strengthen the muscles, and restore function in the affected arm.
Recovery from Surgery for Tennis Elbow
Recovery from tennis elbow surgery can vary depending on the specific surgical technique used, the individual’s overall health, and their commitment to rehabilitation. Here are some general aspects to consider regarding the recovery process:
Postoperative Care
Following surgery, the surgical site will be bandaged, and the arm may be placed in a splint or brace to provide support and protection. The surgeon will provide specific instructions on how to care for the incision site, manage pain, and reduce swelling.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a vital component of the recovery process. The therapist will guide you through exercises and stretches aimed at gradually restoring range of motion, improving strength, and promoting healing. The therapist may also use techniques such as manual therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to aid in recovery.
Gradual Return to Activities
It’s important to gradually reintroduce activities and movements that involve the affected arm. Your surgeon and physical therapist will provide guidelines on when and how to safely resume activities such as lifting, gripping, and sports participation. It’s crucial to follow these guidelines to prevent reinjury and promote a successful recovery.
Pain Management
It is common to experience some discomfort and pain following surgery. Your doctor may prescribe pain medications or recommend over-the-counter pain relievers to manage any postoperative pain. Following the recommended pain management plan will help you stay comfortable during the recovery process.
Timeframe
The recovery time can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the surgery. Generally, it may take several weeks to a few months to fully recover from tennis elbow surgery. It’s important to be patient and not rush the healing process to avoid complications or setbacks.
During the recovery period, it’s essential to attend all follow-up appointments with your surgeon and adhere to their recommendations. They will monitor your progress, assess the healing of the surgical site, and make any necessary adjustments to your rehabilitation plan.
Alternative Treatments and Complementary Therapies
Several alternative treatments and complementary therapies may support conventional approaches to managing tennis elbow which can heal soft tissue from repetitive stress. These include:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Therapeutic ultrasound
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT)
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or Stem Cell Therapy
- Shock Wave Therapy
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before pursuing these treatments to ensure their safety and effectiveness for your specific situation.
How to Prevent Tennis Elbow
Proper Warm-up and Stretching
Before engaging in any physical activity that involves repetitive arm movements, it’s essential to warm up properly. Start with light aerobic exercises to increase blood flow to the muscles, followed by specific stretches that target the forearm, wrist, and hand muscles. This prepares the muscles for activity and reduces the risk of injury.
Correct Technique and Form
Whether you’re playing tennis, painting, or engaging in any activity that involves repetitive arm movements, using proper technique and form is crucial. Incorrect form can put unnecessary strain on the tendons and increase the risk of developing tennis elbow. Seek guidance from a qualified instructor or coach to ensure you’re using the correct technique for your chosen activity.
Equipment Considerations
Using appropriate equipment is essential in preventing tennis elbow. For sports such as tennis or golf, choose a racket or club with the right grip size and flexibility. Using equipment that is too heavy or has an improper grip can strain the forearm muscles and tendons. Additionally, consider using vibration-dampening devices or materials on your equipment to reduce the impact on your arm.
Gradual Training and Strength-Building
Avoid overexertion and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities. Sudden increases in training volume or intensity can overload the tendons and lead to injury. Incorporate progressive strength-training exercises for the forearm muscles, ensuring a balanced approach that targets both the extensor and flexor muscles.
Recovery and Rest Periods
Allowing adequate recovery and rest periods is essential for maintaining optimal muscle and tendon health. Alternate between periods of activity and rest, and listen to your body. If you experience any pain or discomfort, take a break and allow your muscles and tendons to recover before resuming activity.
Regular Maintenance Exercises
Even if you’ve successfully recovered from tennis elbow, it’s important to continue with regular maintenance exercises to prevent its recurrence. Incorporate specific exercises that target the forearm, wrist, and hand muscles into your routine. This helps maintain muscle balance, flexibility, and strength, reducing the risk of reinjury.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tennis Elbow
What are the main symptoms of tennis elbow?
Tennis elbow typically presents with pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow. Other common symptoms include weakened grip strength, difficulty fully extending the forearm, elbow stiffness in the morning, and swelling or inflammation around the elbow.
How is tennis elbow diagnosed by a healthcare professional?
Healthcare professionals diagnose tennis elbow through a physical examination, discussing symptoms and medical history. They may also perform imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to rule out other conditions and may conduct specific tests to assess strength and range of motion in the arm.
Can tennis elbow affect non-athletes or people who don’t play tennis?
Yes, tennis elbow can affect individuals who engage in repetitive arm movements, regardless of whether they play tennis or participate in sports. Occupations that involve repetitive actions, such as painting, plumbing, or computer work, can also contribute to the development of tennis elbow.
Are there any home remedies that can help relieve tennis elbow pain?
Several home remedies may help relieve tennis elbow pain, including applying ice packs to the affected area, taking over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), using topical pain-relieving creams or gels, and practicing gentle stretches and exercises as recommended by a healthcare professional.
How long does it take to recover from tennis elbow?
The recovery time for tennis elbow varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s adherence to treatment and rehabilitation. In mild cases, recovery may take a few weeks to a couple of months, while more severe cases may require several months to a year or longer for full recovery.
Is surgery the only solution for severe cases of tennis elbow?
Surgery is typically considered as a last resort for severe cases of tennis elbow that have not responded to conservative treatments. Most cases of tennis elbow can be effectively managed with a combination of rest, physical therapy, pain management techniques, and lifestyle modifications. Surgery is only recommended when other options have been exhausted.
Learn more in this short video covering the anatomy of our elbow, the causes of this painful condition, and possible treatment options.
Keep up to date on future webinars and events and receive information on living a healthy and pain free life from our providers by joining our monthly newsletter. Click below to sign up!